VIVO Pathophysiology
Physiologic Effects of Insulin
Stand on a streetcorner and ask people if they know what insulin is, and many will reply, "Doesn't it have something to do with blood sugar?" Indeed, that is correct, but such a response is a bit like saying "Mozart? Wasn't he some kind of a musician?"
Insulin is a key player in the control of intermediary metabolism, and the big picture is that it organizes the use of fuels for either storage or oxidation. Through these activities, insulin has profound effects on both carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, and significant influences on protein and mineral metabolism. Consequently, derangements in insulin signalling have widespread and devastating effects on many organs and tissues.
The Insulin Receptor and Mechanism of Action
Like the receptors for other protein hormones, the receptor for insulin is embedded in the plasma membrane. The insulin receptor is composed of two alpha subunits and two beta subunits linked by disulfide bonds. The alpha chains are entirely extracellular and house insulin binding domains, while the linked beta chains penetrate through the plasma membrane.
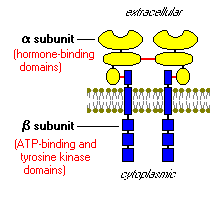
The insulin receptor is a tyrosine kinase. In other words, it functions as an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to tyrosine residues on intracellular target proteins. Binding of insulin to the alpha subunits causes the beta subunits to phosphorylate themselves (autophosphorylation), thus activating the catalytic activity of the receptor. The activated receptor then phosphorylates a number of intracellular proteins, which in turn alters their activity, thereby generating a biological response.
Several intracellular proteins have been identified as phosphorylation substrates for the insulin receptor, the best-studied of which is insulin receptor substrate 1 or IRS-1. When IRS-1 is activated by phosphorylation, a lot of things happen. Among other things, IRS-1 serves as a type of docking center for recruitment and activation of other enzymes that ultimately mediate insulin's effects. A more detailed look at these processes is presented in the section on Insulin Signal Transduction.
Insulin and Carbohydrate Metabolism
Glucose is liberated from dietary carbohydrate such as starch or sucrose by hydrolysis within the small intestine, and is then absorbed into the blood. Elevated concentrations of glucose in blood stimulate release of insulin, and insulin acts on cells thoughout the body to stimulate uptake, utilization and storage of glucose. The effects of insulin on glucose metabolism vary depending on the target tissue. Two important effects are:
1. Insulin facilitates entry of glucose into muscle, adipose and several other tissues. The only mechanism by which cells can take up glucose is by facilitated diffusion through a family of hexose transporters. In many tissues - muscle being a prime example - the major transporter used for uptake of glucose (called GLUT4) is made available in the plasma membrane through the action of insulin.
When insulin concentrations are low, GLUT4 glucose transporters are present in cytoplasmic vesicles, where they are useless for transporting glucose. Binding of insulin to receptors on such cells leads rapidly to fusion of those vesicles with the plasma membrane and insertion of the glucose transporters, thereby giving the cell an ability to efficiently take up glucose. When blood levels of insulin decrease and insulin receptors are no longer occupied, the glucose transporters are recycled back into the cytoplasm.
It should be noted here that there are some tissues that do not require insulin for efficient uptake of glucose: important examples are brain and the liver. This is because these cells don't use GLUT4 for importing glucose, but rather, another transporter that is not insulin-dependent.
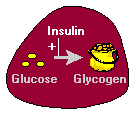
2. Insulin stimulates the liver to store glucose in the form of glycogen. A large fraction of glucose absorbed from the small intestine is immediately taken up by hepatocytes, which convert it into the storage polymer glycogen.
Insulin has several effects in liver which stimulate glycogen synthesis. First, it activates the enzyme hexokinase, which phosphorylates glucose, trapping it within the cell. Coincidently, insulin acts to inhibit the activity of glucose-6-phosphatase. Insulin also activates several of the enzymes that are directly involved in glycogen synthesis, including phosphofructokinase and glycogen synthase. The net effect is clear: when the supply of glucose is abundant, insulin "tells" the liver to bank as much of it as possible for use later.
3. A well-known effect of insulin is to decrease the concentration of glucose in blood, which should make sense considering the mechanisms described above. Another important consideration is that, as blood glucose concentrations fall, insulin secretion ceases. In the absense of insulin, a bulk of the cells in the body become unable to take up glucose, and begin a switch to using alternative fuels like fatty acids for energy. Neurons, however, require a constant supply of glucose, which in the short term, is provided from glycogen reserves.
When insulin levels in blood fall, glycogen synthesis in the liver diminishes and enzymes responsible for breakdown of glycogen become active. Glycogen breakdown is stimulated not only by the absense of insulin but by the presence of glucagon, which is secreted when blood glucose levels fall below the normal range.
Insulin and Lipid Metabolism
The metabolic pathways for utilization of fats and carbohydrates are deeply and intricately intertwined. Considering insulin's profound effects on carbohydrate metabolism, it stands to reason that insulin also has important effects on lipid metabolism, including the following:
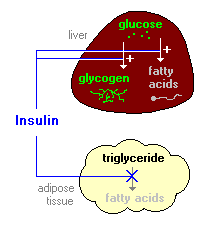
1. Insulin promotes synthesis of fatty acids in the liver. As discussed above, insulin is stimulatory to synthesis of glycogen in the liver. However, as glycogen accumulates to high levels (roughly 5% of liver mass), further synthesis is strongly suppressed.
When the liver is saturated with glycogen, any additional glucose taken up by hepatocytes is shunted into pathways leading to synthesis of fatty acids, which are exported from the liver as lipoproteins. The lipoproteins are ripped apart in the circulation, providing free fatty acids for use in other tissues, including adipocytes, which use them to synthesize triglyceride.
2. Insulin inhibits breakdown of fat in adipose tissue by inhibiting the intracellular lipase that hydrolyzes triglycerides to release fatty acids.
Insulin facilitates entry of glucose into adipocytes, and within those cells, glucose can be used to synthesize glycerol. This glycerol, along with the fatty acids delivered from the liver, are used to synthesize triglyceride within the adipocyte. By these mechanisms, insulin is involved in further accumulation of triglyceride in fat cells.
From a whole body perspective, insulin has a fat-sparing effect. Not only does it drive most cells to preferentially oxidize carbohydrates instead of fatty acids for energy, insulin indirectly stimulates accumulation of fat in adipose tissue.
Other Notable Effects of Insulin
In addition to insulin's effect on entry of glucose into cells, it also stimulates the uptake of amino acids, again contributing to its overall anabolic effect. When insulin levels are low, as in the fasting state, the balance is pushed toward intracellular protein degradation.
Insulin also increases the permiability of many cells to potassium, magnesium and phosphate ions. The effect on potassium is clinically important. Insulin activates sodium-potassium ATPases in many cells, causing a flux of potassium into cells. Under certain circumstances, injection of insulin can kill patients because of its ability to acutely suppress plasma potassium concentrations.
Insulin Deficiency and Excess Diseases
Diabetes mellitus, arguably the most important metabolic disease of man, is an insulin deficiency state. It also is a significant cause of disease in dogs and cats. Two principal forms of this disease are recognized:
- Type 1 or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is the result of a frank deficiency of insulin. The onset of this disease typically is in childhood. It is due to destruction pancreatic beta cells, most likely the result of autoimmunity to one or more components of those cells. Many of the acute effects of this disease can be controlled by insulin replacement therapy. Maintaining tight control of blood glucose concentrations by monitoring, treatment with insulin and dietary management will minimize the long-term adverse effects of this disorder on blood vessels, nerves and other organ systems, allowing a healthy life.
- Type 2 or non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus begins as a syndrome of insulin resistance. That is, target tissues fail to respond appropriately to insulin. Typically, the onset of this disease is in adulthood. Despite monumental research efforts, the precise nature of the defects leading to type II diabetes have been difficult to ascertain, and the pathogenesis of this condition is plainly multifactorial. Obesity is clearly a major risk factor, but in some cases of extreme obesity in humans and animals, insulin sensitivity is normal. Because there is not, at least initially, an inability to secrete adequate amounts of insulin, insulin injections are not useful for therapy. Rather the disease is controlled through dietary therapy and hypoglycemic agents. However, a substantial number of those with type 2 diabetes progress to requiring insulin.
Hyperinsulinemia or excessive insulin secretion is most commonly a consequence of insulin resistance, associated with type 2 diabetes or the metabolic syndrome. More rarely, hyperinsulinemia results from an insulin-secreting tumor (insulinoma) in the pancreas. Hyperinsulinemia due to accidental or deliberate injection of excessive insulin is dangerous and can be acutely life-threatening because blood levels of glucose drop rapidly and the brain becomes starved for energy (insulin shock).
Last updated February 2019. Send comments to Richard.Bowen@colostate.edu
A Bosnian translation of this page was created by Amina Dugalic and is available at Bosnian translation
A Finnish translation of this page was created by Elsa Jansson and is available at Finnish translation
A French translation of this page was created by Mathilde Guibert and is available at French translation
A Latvian translation of this page was created by Margareta Sliwka and is available at Latvian translation
A Russian translation of this page was created by Olha Fiodorova and is available at Russian translation
A Slovakian translation of this page was created by Katarina Hornik and is available at Slovakian translation
A Swedish translation of this page was created by David Mucchiano and is available at Swedish translation
A Ukrainian translation of this page was created by Anna Matesh and is available at Ukrainian translation